
VOLUME 62 : 2014
VOLUME 62 : 2014
ACTA MANILANA publishes research and innovation in the different branches of the natural and applied sciences. It reports significant development in the discipline, and novel applications, unconfined by the traditional coverage of the disciplines.
Molecularly imprinted potentiometric sensor for surfactant based on electrosynthesized polyaniline
Page 61-67
Francis G. Biñas & Fortunato Sevilla III
ARTICLE DOI: https://doi.org/10.53603/actamanil.62.2014.esfw5424
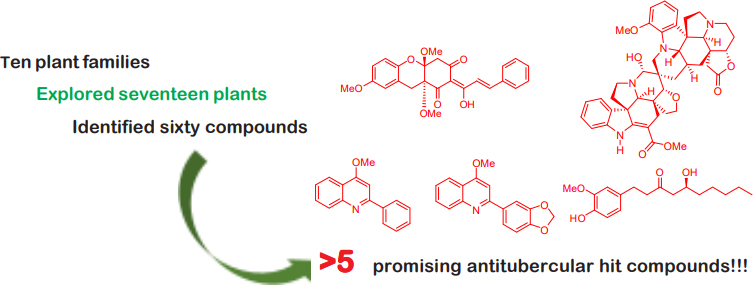
Graphical Abstract
Abstract
A potentiometric sensor for sodium dodecylsulfate (SDS) was developed based on molecularly-imprinted polyaniline. The molecularly-imprinted polymer was synthesized through a potentiostatic electropolymerization of aniline monomer in the presence of the template SDS molecule at a constant potential of 0.8 V. The polymerization parameters determined the analytical performance of the polyaniline reagent phase. The optimized electropolymerization process provided a sensor with sensitivity of 45.54±6 mV/decade, working concentration range of 3×10–6 M to 1×10–2 M SDS, correlation coefficient (r2) of 0.993 and with a limit of detection 1×10–5 M DS–. The sensor response is reproducible with a mean RSD of 8.08% from 3×10–6 M to 3×10–3 M SDS. Selectivity studies using the fixed primary ion method proved the higher selectivity of the synthesized polymer for SDS over inorganic salts and fatty acid salts.
Keywords: molecularly imprinted polyaniline, potentiometric sensor, sodium dodecysulfate
FOLLOW US
-
Research Center for the Natural and Applied Sciences
Thomas Aquinas Research Complex Building
University of Santo Tomas España, 1015 Manila, Philippines -
TL: (+63 2) 3406-1611 local 4037
DL: (+63 2) 8731-4031 - actamanilana@ust.edu.ph

© 2021 University of Santo Tomas, Acta Manilana. All rights reserved
Powered by: Communications Bureau