
VOLUME 64 : 2016
VOLUME 64 : 2016
ACTA MANILANA publishes research and innovation in the different branches of the natural and applied sciences. It reports significant development in the discipline, and novel applications, unconfined by the traditional coverage of the disciplines.
Natural products-based discovery of antitubercular agents from Philippine medicinal plants — A review
Page 87-98
Allan Patrick G. Macabeo, Oliver B. Villaflores, Scott G. Franzblau, & Ma. Alicia M. Aguinaldo
ARTICLE DOI: https://doi.org/10.53603/actamanil.64.2016.xkry2962
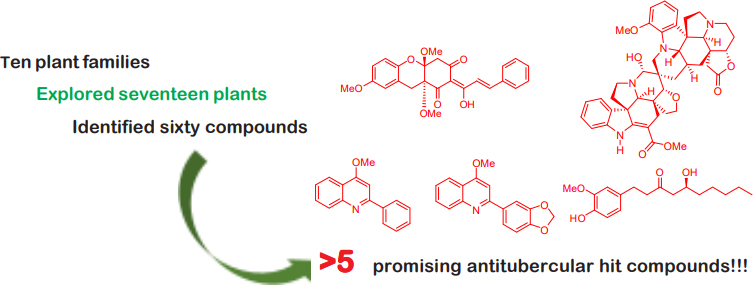
Graphical Abstract
Abstract
Tuberculosis is one of the leading causes of death worldwide, more than HIV and malaria. New TB cases are emerging, including multidrug-resistant TB. The development of antimycobacterial assays led to the discovery of secondary metabolites that elicit promising inhibitory activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This review covers literature published from 1999 to 2014 about natural products from Philippine medicinal plants with reported growth inhibitory activity in vitro against M. tuberculosis H37Rv. The antitubercular compounds were grouped according to plant family and/or chemotype. Some exhibited structural significance but with low inhibitory activity (MICs of >128 mg/mL). While other previously reported compounds that were re-isolated exhibited anti-TB activity.
Keywords: antitubercular, anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Philippine medicinal plants, natural products
FOLLOW US
-
Research Center for the Natural and Applied Sciences
Thomas Aquinas Research Complex Building
University of Santo Tomas España, 1015 Manila, Philippines -
TL: (+63 2) 3406-1611 local 4037
DL: (+63 2) 8731-4031 - actamanilana@ust.edu.ph

© 2021 University of Santo Tomas, Acta Manilana. All rights reserved
Powered by: Communications Bureau